
In 2012, a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) achieved satisfactory results in the ImageNet classification work 17. These new algorithms significantly reduce the workload of human experts, and can extract certain features that are difficult for humans to recognize. Although certain researches achieved satisfactory results, only a few numbers of high-quality images were tested.ĭeep learning has developed in recent years, and is capable of automatically extracting image features using the original pixel information as input. This constitutes a large workload, and the performance of image recognition significantly depends on the quality of the extracted features. However, the majority of these algorithms often conduct an image enhancement process before segmentation and feature extraction, and the image features are usually extracted manually. In their studies, mathematical morphology 10, active contour 11 or level-set method 15 was used for teeth segmentation, while Fourier descriptors 9, contours 13, textures 15 or multiple criteria 16 were extracted as features, and finally, Bayesian techniques 9, linear models 12, or binary support vector machines 13, 14 were used to perform the classification. To achieve high-accuracy segmentation and classification in dental films, several scholars have developed image-processing algorithms 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16. From this perspective, automatic teeth identification using digitized films is an important task for smart healthcare. The work burden of a dentist and the occurrences of misdiagnosis may be reduced if intelligent dental X-ray film interpretation tools are developed to improve the quality of dental care. Because the film reading work is primarily conducted by dentists, it occupies several valuable clinical hours and may cause misdiagnosis or underdiagnosis owing to personal factors, such as fatigue, emotions, and low experience levels. As an important auxiliary diagnostic tool, a large number of dental X-ray films are photographed daily 8. Dentists usually need to serve numerous patients every day. Further, the oral medical resources are sparse in several developing countries 7. Segmenting teeth from the X-ray film and performing numbering for each tooth, the testing teeth can be compared only with those having the same numbers in the database, thus the computational efficiency and accuracy can be improved. If all the teeth are screened during comparison, the system will encounter a large computational burden and reduction in accuracy.
X-ray films obtained from a cadaver’s teeth are usually compared with their dental film records so that even the identity of a deceased person can still be effectively determined. Therefore, they play an important role in forensic identification 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.
Human teeth are generally hard substances and do not damage easily their shapes can remain unchanged after a person’s death without being eroded. The results indicate that machines already perform close to the level of a junior dentist. Moreover, three dentists are also invited to manually annotate the test dataset (independently), which are then compared to labels obtained by our proposed algorithms. Results demonstrate that both precisions and recalls exceed 90% and the mean value of the IOU between detected boxes and ground truths also reaches 91%. The intersection-over-union (IOU) value between detected and ground truth boxes are calculated to obtain precisions and recalls on a test dataset.

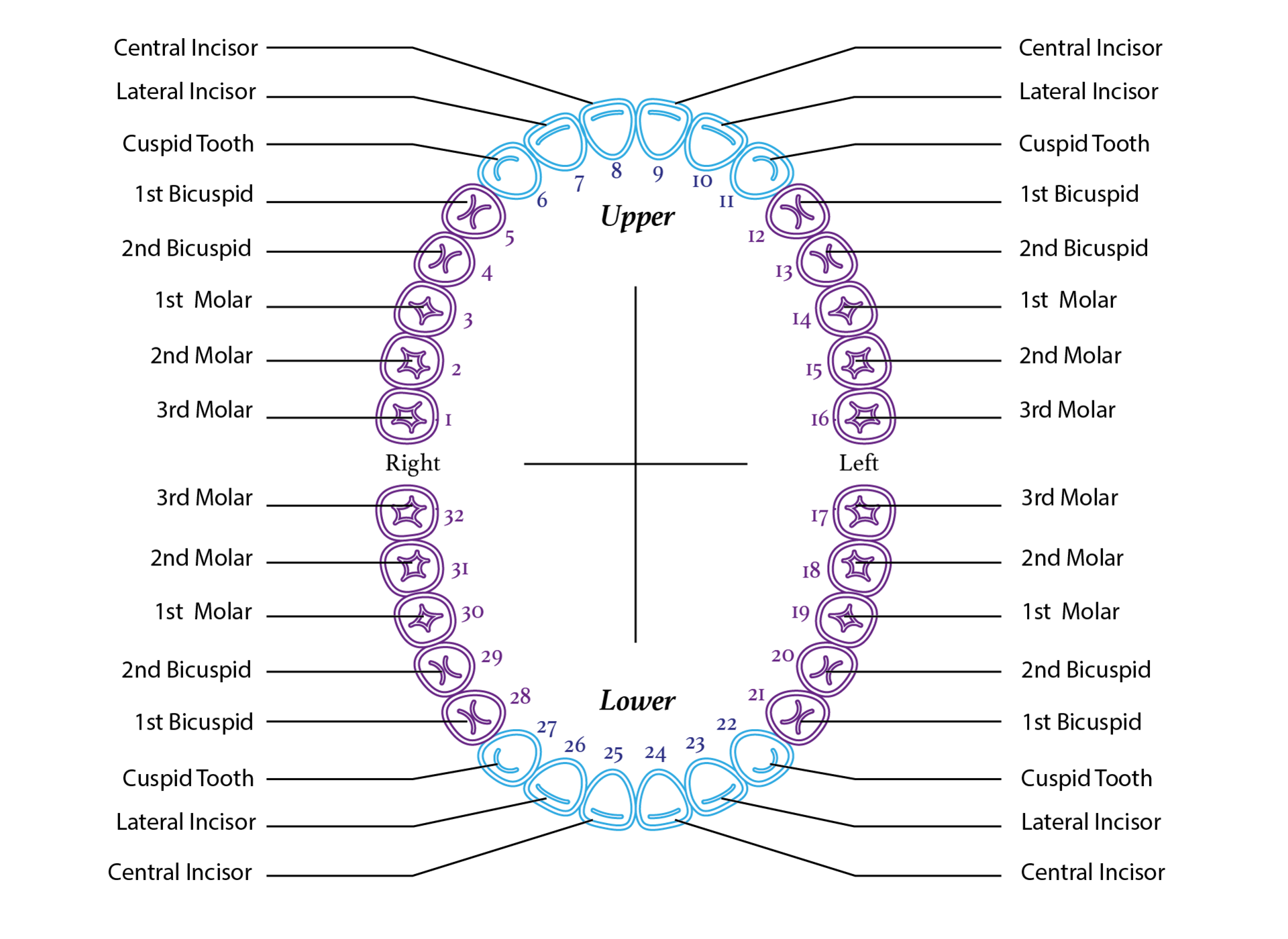
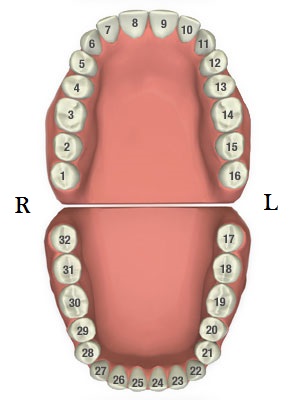
Finally, a rule-base module based on a teeth numbering system is proposed to match labels of detected teeth boxes to modify detected results that violate certain intuitive rules. Next, a neural network model is implemented to detect missing teeth. First, a filtering algorithm is constructed to delete overlapping boxes detected by faster R-CNN associated with the same tooth. To improve detection precisions, we propose three post-processing techniques to supplement the baseline faster R-CNN according to certain prior domain knowledge. We propose using faster regions with convolutional neural network features (faster R-CNN) in the TensorFlow tool package to detect and number teeth in dental periapical films.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
